I. Characteristics of casualties in mining enterprises
Harmful. The occurrence of accidents will cause different degrees of harm and loss in terms of people, property and materials, and will also have certain impact on social stability, economic development and family happiness. Understanding this feature will improve people's sense of safety and social responsibility and safety and economic responsibility.
Danger (ie precursory). Before the accident, the state of the system (person, machine, environment) is unstable, that is, there is an unsafe state, that is, an accident. Knowing this, we can prevent the lax thoughts and complacency, and take appropriate corrective measures to prevent accidents.
Repeatability. That is, the occurrence of an accident has a repeating feature. Mastering this feature has a positive effect on correctly formulating corresponding preventive measures to prevent the recurrence of similar accidents, and also requires people to adhere to the principle of "three not letting go" in the process of accident handling.
Regularity. The time, place and severity of the accident are accidental, but we can analyze the accident statistics to find out the regularity of the accident and provide a strong basis for the development of correct preventive measures.
Preventable. Any accident, as long as we take positive preventive measures in a timely and correct manner, and strive to create a good safe production environment, accidents can be prevented. Recognizing this point has a positive effect on strengthening beliefs and preventing casualties.
Second, the category of mine casualties
Mine casualties are mainly concentrated in against objects, to Cave, falls, collapse, mechanical damage, injury and other vehicles, the 2007 national non-coal mine casualty reason analysis shown in Figure.
3. Analysis and prevention of common accidents in mines
Topping up
Top body slate mine caving accident, according to their scope and the number of casualties cave spalling, and can be divided into a large cave, part roof, turquoise caving three. Roof fall usually occurs in the case of heavy rock and mineral types of exploitation of the mine, metallurgical mine less frequent. Local roofing and loose rocks fall off, and are collectively referred to as roofing accidents.
Such roofing accidents occur in the following situations: the broken working face in the roof; the working face of the easy-segregation layer in the bedding, joints and faults; the improper work in the mine, ultra-deep mine, and blasting Work surface.
The occurrence of a roof accident is generally related to many factors such as mine geological conditions, production technology and organization management. According to the statistics of accidents, the reasons for the management of production organizations accounted for 45.6%, accounting for 44.2% of the reasons for material technology, and only 10.2% of accidents caused by risky operations.
(1) Production organization management
1. Mining method selection is unreasonable
Unreasonable selection of mining methods is a major cause of roof failures.
2. The roof support method is unreasonable
The mining face or large section excavation, the unreasonable support method or the untimely support is another main cause of the roof accident. When the roof rock near the working face is relatively broken and the structure is relatively developed, the supporting method is unreasonable or the support is not timely, and the roof is suddenly inflammable and explosive, causing the roof to suddenly fall off or help, causing an accident.
3. Pumice is not handled properly
Most of the loose rocks in the roadway occur within 10 meters from the working face. Most of the loose rocks in the stope occur when the roof of the stope is not too high.
Poor pumice treatment, unqualified workmanship, poor inspection, negligence and even no inspection are one of the causes of accidents. Most of the casualties caused by improper pumice treatment are caused by the lack of comprehensive and meticulous inspection of the top of the working face before pumice treatment, as well as the improper position of the pumice treatment and the unskilled technical skills of the excavator.
4. Improper use of protective equipment
When working in a mine, it is often the case that the roof accident is not enlarged due to the improper use of protective equipment.
5. Personnel management can't keep up
First, there are many new workers used in the underground. They do not understand the underground working environment and lack the training of safety knowledge and skills. The old and the new can't connect together, and they can't promptly and effectively "knock and ask the top" and cause an accident.
Second, the underground management personnel did not pay much attention to the roof management. There was no effective roof management method and supervision and restraint mechanism, so that the roof management was lax, and there was no accident of small roof accidents with casualties. The roof accident with casualties was inevitable.
(2) Preventive measures for roof accidents
1. Adjust the mining process in time to ensure reasonable exposure space and recovery sequence, and effectively control ground pressure.
It is necessary to strengthen the experimental research of mine geological work and mining methods, and continuously improve the original design of mining methods to find efficient and safe mining methods suitable for different geological conditions of the mine, increase mining intensity, and timely process gobs. In order to control the stability of the roof of the stope, it is necessary to have a reasonable mining sequence. Therefore, it is necessary to reasonably determine the order of mining of adjacent two sets of veins; it is necessary to strictly control the exposed area of ​​the stope and mining according to different geological conditions and mining methods. Technical indicators such as the height of the empty area enable the stope to be harvested during the period of stable ground pressure.
2. It is necessary to strengthen the inspection, observation and treatment of the roof to improve the stability of the roof.
The collapse of the top plate is often an important cause of injury. The inspection and treatment of the top stone is a regular and very important task. It is necessary to fix the special person to work according to the prescribed system, in order to ensure the safe production of the roof and prevent the accident of the roof falling off the pine. For some dangerous pits, scientific methods should be used to observe the roof as far as technical and economic conditions permit. At present, domestic economical and simple observation methods include optical stress meter, geophone and rock movement observation. It is necessary to observe and explore the laws of different rock movements and scientifically grasp the roof conditions. For the unstable working roof that has been found, it is necessary to deal with it in time, and use scientific and effective measures (such as spray anchor support) to prevent roof accidents.
3. Scientifically and rationally arrange the location, size, shape and structure of the roadway and stope
It is necessary to avoid the arrangement of the roadway engineering near the geological structure line, because the pressure perpendicular to the geological structure line is the largest, which is the main factor for the change and rupture of the rock mass.
It is necessary to avoid the arrangement of wells and lanes in the vicinity of faults, joints, fracture zones in the layers, muddy interlayers and other geological structures. Because the projects placed in these places are more prone to roofing. If the roadway engineering must pass through these zones, corresponding support measures or special construction plans should also be adopted.
The shape and structure of the roadway and the stope should be as close as possible to the stress distribution requirements of the surrounding rock. Therefore, the roof of the roadway and the stope should be arched as much as possible. Because the secondary stress of surrounding rock is not only related to the original rock stress and lateral pressure coefficient, but also related to the shape of the roadway. When the arch shape is adopted, the construction difficulty is not large and the roof pressure is not too concentrated, and the roof stability is good.
4. Strengthen roof management and improve the technical level of roof management
First, strengthen the training of safety education and safety technology knowledge, improve the technical level of safety management personnel at all levels, establish the idea of ​​"safety first", obey the rules and discipline, and establish a roof management system for group inspection, group defense, and group governance. Special crowbars are provided at each work surface, and special personnel or concurrent management personnel are set up to be responsible for the risk-recovery work of each work surface, set up warning signs, do a good job of handover system and be listed as key dangerous source management.
Secondly, combined with the actual situation of the mine, summing up the experience and lessons of roof management, from the provision of geological data, well design, well maintenance technology, construction management, develop a complete set of roof construction management standards for scientific and effective management of the roof provide technical support.
(3) Self-help and mutual rescue in the event of a roof accident
1. Self-rescue measures for disaster avoidance when the roof is falling
(1) Retreat to a safe place quickly. When it was found that there was a sign of impending roofing at the workplace, and it was difficult to take measures to prevent the roof of the face from falling, the best way to avoid it was to quickly leave the danger zone and retreat to a safe place.
(2) When you are in distress, you should rely on the body to stand up or go to the raft to avoid the disaster. Judging from the actual situation of roof collapse in the mining face, it is rare for the roof to fall along the rock wall. Therefore, when a roof collapse is too late to retreat to a safe place, the person in distress should rely on the rock to stand up and avoid the disaster, but pay attention to help the wall to help hurt people. In addition, the pillar may be crushed or destroyed when the roof is lowered, but it is generally impossible to crush or push down the quality raft. Therefore, if the position of the person in distress is close to the raft, you can evacuate to the raft to avoid the disaster.
(3) Immediately after the distress, a distress signal is issued. The damage caused by the roof is mainly caused by bruises, burial or blockage. After the basic stability of the fall, the person in distress should immediately call and knock (such as hitting the material, the rock may cause a new fall, then can not be beaten, can only call) and other methods, issuing a regular, uninterrupted call for help, So that the ambulance personnel and the evacuation personnel can understand the disaster situation and organize the troops to carry out the rescue.
(4) Persons in distress should actively cooperate with external rescue work. Those who are buried under rocks and materials after the topping should not panic. When conditions are not allowed, they should not use the violent struggle to escape the danger and cause the accident to expand. Persons who are blocked by the roof shall be organized to maintain their own safety in the place of distress, construct escape routes, cooperate with external rescue work, and create favorable conditions for early escape.
2. Rescuing the measures taken by the person who is under pressure to bury the person in distress
(1) Guarantee the safety of rescue personnel. Rescue work should be carried out under the leadership of the disaster area and under the command of experienced workers. Rescue personnel should check the condition of the bracket near the roof and find that there are pillars that are damaged, twisted and deformed, and should be disposed of immediately to ensure the safety of the rescue personnel, and to set up a smooth and safe retreat.
(2) Support the roof at a suitable location. According to the situation of the roof falling, under the premise of ensuring the safety of the rescue personnel and the convenience of rescue, the roof is supported according to local conditions. When the top of the mining face is top-buried, the truss beam socket, the metal roof beam, the truss beam socket, and the single eye shed can be used for treatment. The gaps on the shed beams should be erected with wooden rafts to the top, and the backs should be tightly inserted to prevent further expansion of the roof.
(3) Rescue buried pressure personnel. After checking that the erected bracket is firm and reliable, it is necessary to assign a person to observe the roof to clean up the falling rocks in the vicinity of the buried personnel until the person in danger is rescued from the buried pressure. During the rescue process, long wooden sticks can be used to deliver drinks and food to those in distress. When cleaning up the falling rocks, use the tools carefully to avoid harming the people in distress. If the person in distress is crushed by large rocks, tools such as hydraulic lifting cushions, hydraulic jacks or jacks should be used to lift large rocks and rescue people quickly.
3. Self-rescuing measures for avoiding disasters in the headway of the headway
(1) Persons in distress should face up to the disasters that have occurred, and should not panic, and firmly believe that leaders and workers will actively carry out rescue. It should be quickly organized, and actively follow the instructions of the team leader and experienced workers in the disaster area, work together to minimize the oxygen consumption in the physical and isolation areas, and use the water, food and lighting in a planned way to avoid long-term avoidance. Preparation for the disaster.
(2) If there is a telephone at the location where the person is trapped, he should immediately report the disaster situation, the number of people in distress and the planned self-rescue measures. Otherwise, a regular call for help should be issued by tapping on rails, pipes and rocks. And knocking once every certain time, uninterrupted signal, so that rescue personnel can understand the disaster situation and organize forces to rescue.
(3) Maintain the brackets for the reinforcement of the landing site and the personnel shelter, and often send people to check to prevent further expansion of the roof, and to ensure the safety of the blocked personnel when avoiding disasters.
(4) If there is a pressure air duct at the location where the person is trapped, the air duct should be opened to deliver fresh air to the trapped person. But be careful to keep warm.
Blasting accident
Blasting is a chemical reaction characterized by a rapid reaction that generates a large amount of gas and produces a large amount of heat. Blasting is a destructive behavior and a means to provide ore and rock for various purposes; the demolition of buildings and structures, the migration of mountains and fields, and the construction of water conservancy. The wide application of blasting has greatly improved labor productivity and speeded up the progress of the project. In short, people use the energy released by explosives to benefit mankind. However, due to mistakes in use, blasting accidents occur frequently, which brings great losses to the national property and people's lives.
The blasting accident has two meanings: one refers to the public injury caused by blasting, causing casualties, damage to buildings and structures; the second refers to the self-destruction accident during the blasting operation, resulting in blind cannons. The main cause of the accident was caused by violation of blasting safety regulations, illegal operations, and insufficient understanding of blasting safety in blasting operations.
The main cause of the blasting itself is the explosion-proof accident, such as the network does not explode, leaving the blind cannon, etc. The main reason is the poor quality of the blasting material, the deterioration of the moisture, the damage of the line during the construction, the connection error, the leakage point, the leakage connection and so on.
Prevention of blasting accidents:
1. General regulations
The blasting operator must obtain the qualification of the blaster; all blasting must be prepared with a blasting design book or a blasting specification. The design book or specification should have a specific blasting method, blasting sequence, charge amount, ignition or connection method, and warning. Safety measures, etc.; during the blasting process, unrelated personnel must be evacuated. Blasting must be carried out in accordance with the approved blasting design book or blasting instructions; strictly observe the safety regulations and safe operating rules of blasting operations.
2, charging, filling
It must be carried out before the charge for clean-up and acceptance of blast holes, using bamboo sticks charge, prohibit charge with an iron rod. When charging, fireworks are prohibited and open flames are prohibited. In the expansion of the pot blasting, the time interval of the expansion of the pot must be greater than 15mm, to prevent the blasthole temperature is too high, leading to early explosion. In addition to the deep bare blasting, any blasting must be filled with the pharmacy. The tamping should be carried out with great care and must not damage the detonating network and the line.
3, alert
Sound and visual signals must be generated simultaneously before blasting so that people in the danger zone can clearly hear and see. Underground blasting should set up sentries on the relevant passages. Ground blasting should set up sentries at the boundary of the dangerous area to make all The channels are under surveillance. All personnel in the blasting danger zone should be evacuated.
4, ignition, wiring, detonation
If the fuse is used to ignite and detonate, no less than two people should perform the blasting operation, and it must be ignited by a fuse or a special ignition device. When a single ignition occurs, the number of consecutive ignitions of one person shall not exceed 5 underground explosions, and the number of open-air explosions shall not exceed 10. The length of the fuse shall be such that after the completion of the fuse, the personnel can be evacuated to a safe place, but not shorter than 1 meter.
When the electric detonator is detonated, the electric detonator must be turned on one by one, and the electric detonator used for the same blasting network should be the same model of the same factory. Before the main line of blasting is connected with the blasting power supply, the total resistance value of the whole line must be measured. The error between the total resistance value and the actual calculated value must be less than ± 5%. Otherwise, the connection is prohibited. Large blasting must use a double detonation line. When a mine with a risk of coal dust and gas explosion is used for electric detonation, only an explosion-proof detonator is used as the detonating power source.
5, post-explosion check
After the cannon is fired, the open-air blasting shall be no less than 5 minutes, and the underground blasting shall be no less than 15 minutes (after the ventilation and blowing of the gunpowder shall be ventilated). After confirming the safety of the blasting site, the de-alerting signal shall be issued after the blasting person in charge or the blasting squad leader agrees. The authorized personnel enter the blasting site.
6, blind cannon processing
The blind cannons produced by the detonation include the unexploded blastholes of the detonator (the rifle) and the blastholes (the rifles) of the detonator that have not exploded. The production of blind cannons in blasting not only affects the blasting effect, but if it is not discovered or handled improperly, the potential danger is extremely high, often caused by accidental blind cannons, disfigured eyes or frictional vibrations causing blind cannons to explode.
Therefore, if blind cannons and suspected blind cannons are found, they should be reported immediately and dealt with promptly. If they cannot be dealt with in time, obvious signs should be set and corresponding safety measures should be taken to prohibit the extraction or pulling out of the explosive charge, and it is strictly forbidden to kill the eyes. The main methods of blind cannon are:
(1) After the inspection confirms that the detonation line of the blasthole is intact and the leakage is caused by the leakage or the ignition, the detonation can be performed again.
(2) The parallel eye charge is detonated. For shallow blasting, parallel eye distance blind blasthole shall not be less than 0.3m, and deep hole blasting parallel eye distance blind blasthole shall not be less than 10 times the blasthole diameter.
(3) Using a tool made of wood, bamboo or other non-flaming materials, gently pry out most of the stuffing in the blasthole and use a concentrating drug pack to induce the blast.
(4) If the explosive used is a non-water-resistant ammonium nitrate explosive, a part of the stuffing may be taken out and water is poured into the hole to invalidate the explosive.
High fall accident
1. "Three treasures" protective measures
Safety helmets, safety belts and safety nets are safety "three treasures". At the job site, personnel should: 1 wear safety helmets for workers entering the job site; 2 high-altitude workers must wear seat belts; 3 safety nets must be provided below the high-altitude operation points.
2. "Protection, edge, wellhead" protection
The frontier, the hole, the wellhead guardrail, and the protective cover are all installed in most of the operation sites, but there are problems such as insufficient standardization, easy movement or poor effect. Therefore, it is necessary to do all kinds of protection of the edge and the wellhead at the job site. At the same time, it is recommended that some high-rise fall protection facilities should be specially researched and produced. For the protective cover of the hole, some sizes for different hole sizes can be developed. The "safety cover" can neither be moved nor clearly marked. Such safety facilities are very beneficial for preventing falling from high places.
3. Put the nine lanes off
(1) Material is closed, and materials (such as boards, crepe steel, etc.) are selected in strict accordance with the specified quality and specifications.
(2) When the size is off, rods, crossbars, railings, etc. must be set up according to the specified spacing. For the logs and boards used in each platform, new materials with better quality must be selected, and insects and broken wood should not be used.
(3) The paving is closed, the framing board must be full, there should be no gaps, probe boards, flying spring boards, and the board debris should be removed frequently to keep it clean and flat. The wooden springboard must be 5cm thick.
(4) Column protection, 1m high railings and standing nets on the outside of the scaffolding and on both sides of the ramp.
(5) If the connection is closed, the scissors support and support must be provided according to the regulations. The shelf above 7m must be firmly connected and must not be shaken.
(6) Load-bearing, uniform load of scaffolding, no more than 27MPa. If overloaded, reinforcement measures should be taken to ensure safety.
(7) Up and down, you must set up a horse or ladder for the workers to go up and down the shelf. Construction workers are strictly forbidden to climb up and down from the frame, causing a fall accident.
(8) Picking up the beam, hanging the blue footer, in addition to the hanging basket according to the provisions of processing, set up the basket and the net, the beam should be flat and firm. The diameter of the round wood (small head) shall not be less than 10 cm, and the thickness of the square board shall be uniform and shall not be less than 5 cm;
(9) Inspection and inspection. After all kinds of shelves are set up, it is necessary to check and confirm that the safety is qualified before operation.
4. Ladder
Because of the high altitude drop accidents that occur when the ladder is not strong, it is required to:
(1) The ladder should be firmly fixed. The main pedestrian ladder must be made of 35-45 mm angle steel. The material for the ladder must be made of 16-18mm round steel or crepe steel. The distance between the steps should not exceed 30. For centimeters, the height of each ladder shall not exceed 3 meters; the distance between piles shall not exceed 2 meters.
(2) step 30cm-40cm;
(3) An angle of 60°-70° with the ground;
(4) The foot should have anti-slip measures;
(5) The top end is tied firmly or a special person escalator is provided.
5. Seriously implement the rules and regulations
In terms of preventing high-altitude fall accidents, the main needs to be strengthened are:
1 check and acceptance of facilities and materials used for high-altitude operations, and re-inspection of turnover use;
2 For some links that are prone to high-level fall accidents, it is classified as dangerous source management, and a special person is required to check at any time;
3 Strengthen the inspection during the use of the fall protection facility. The content of inspection and the number of inspections shall be stipulated, so that personnel shall be implemented and the responsibilities shall be clear Eliminate the hidden dangers caused by changes in these facilities.
6. Specific measures
(1) Shafts, patios, slides, etc. used must be closed in time; temporary safety measures must be taken for temporary deactivation, and closed in time; suspended or standby wells and cutting wells should be temporarily closed or fall-proof after development. ;
(2) The used wellhead must be equipped with fences, grids, lighting, warning signs and personnel safety passages to prevent personnel from falling; the shafts should be dug and closed, and the wellheads must be tightly sealed and have a solid interlocking safety door. Keep clean near the wellhead. No debris;
(3) Connections for lifting wells, pedestrian wells and middle sections shall have fences, safety gates, sidewalks, lighting and car-stoppers; special pedestrian wells shall have qualified ladders and ladders;
(4) Mitsui operations and wells must have reliable contact signals and fall arrest measures;
(5) Suspension discs, hanging tanks, lifting platforms, work tables (sheds), safety sheds, etc. used in aerial work must be strong and secure; the joints are free from deformation and have a solid and reliable locking device. Compliance with safety regulations;
(5) Lifting platforms and walking platforms for high-altitude operations and high-rise work sites; solid cliffs must be provided at the cliff steep slopes beside the mine mountain sidewalks;
(6) For the production, living needs of the pits, rafts, pools and high-rises, holes, elevators, etc. must have a fence or cover;
(7) Jian'an project must have solid scaffolding, pedals, fences, safety nets, scaffolding, etc. in accordance with the regulations, and must be operated according to the regulations. It is strictly forbidden to throw from top to bottom;
(8) The lifting equipment used for high-rise buildings must have reliable limit, braking, lightning protection grounding devices, and regularly check the steel wire ropes and connecting parts and safety brake devices;
(9) Personnel in high-altitude operations (high-rise construction, hanging tanks, wellbore installation, maintenance, etc.) must undergo health check and safety training before they can be employed. You must wear a safety helmet and work on your seat belt.
Mechanical injury accident
First, the main reasons for the formation of mechanical injury accidents are:
1. Inspection, inspection of machinery, handling of hidden dangers and neglect of safety measures. If a person enters the equipment ( ball mill , crusher, etc.) for inspection, inspection, or handling safety hazards, does not cut off the power supply, does not hang up the warning sign, and does not have special personnel supervision and other measures, causing serious consequences. Some accidents were caused by misjudgment due to factors such as the timing of the power switch or the occurrence of temporary power outages. There are also some power outages, but it does not wait until the inertia of the equipment stops completely and starts to work, which also has serious consequences;
2. Lack of safety devices. If there are mechanical transmission belts, gear machines, couplings close to the ground, pulleys, flywheels, etc., there are no intact guards for the vulnerable parts of the human body; there are missing guardrails and cover plates for the entrance holes, feed ports, and cage cages, etc. Warning signs, when a person accidentally touches these parts, it will cause an accident;
3. The layout of the power switch is unreasonable. One is that there is no emergency to stop immediately; the other is that several mechanical switches are set together, which can easily cause serious consequences caused by accidental opening of the machine;
4. Self-made or arbitrarily modified mechanical equipment, does not meet safety requirements;
5. In the mechanical operation, cleaning, jamming, waxing, etc. (such as cleaning the waste on the running belt);
6. Arbitrarily enter the hazardous operation area of ​​the machine operation (sampling, working, borrowing, picking, etc.);
7. Personnel who do not have mechanical quality are employed or other personnel mobilize the machinery.
Second, preventive measures to prevent mechanical injury accidents:
1. The inspection machinery must strictly implement the system of prohibiting the closing of the warning sign and the guardianship of the special person. After the mechanical power is turned off, it must be confirmed that the inertia operation has been completely eliminated before the work can be performed. After the mechanical overhaul is completed, before the test run, the site must be carefully examined to confirm that all the personnel of the mechanical parts have been completely evacuated before the card can be closed. When repairing the test drive, it is strictly forbidden to stay in the equipment to pick up the car;
2. Machines that are in direct contact with human hands must have an emergency brake device. The position of the brake button must be accessible to the operator at any time within the scope of the mechanical operation; the transmission parts of the mechanical equipment must have reliable protection devices; The hole, the feeding port, the screw conveyor and other parts must have a cover plate, a guardrail and a warning sign; the working environment is kept clean and hygienic;
3. The layout of each mechanical switch must be reasonable and must meet two standards: one is to facilitate the operator to stop the emergency; the other is to avoid accidentally starting other equipment;
4. For the machinery to clean up the accumulation of materials, smashing materials, belts and other operations, should comply with the system of shutdown and power failure warning signs;
5. It is strictly forbidden for unrelated personnel to enter the mechanical operation site with large risk factors. If the non-machine personnel must enter the work, they must first get in touch with the mechanical author on duty, and have safety measures to agree to enter. 6. Operation of various mechanical personnel must go through Professional training, can master the basic knowledge of the performance of the equipment, passed the examination, and hold the certificate. In the on-the-job operation, it must be carefully operated, strictly enforce the relevant rules and regulations, use labor protection articles correctly, and prohibit unlicensed personnel from starting mechanical equipment.
Gun poisoning
When blasting in a well, blasting explosives tends to generate a gas containing a large amount of toxic components. Due to the narrow working space of the well and the poor ventilation conditions, it is easy to cause the concentration of toxic gases to exceed the standard, posing a serious threat to the health and safety of the construction workers. According to relevant statistics, in the blasting projects at home and abroad, the deaths from gun poisoning accounted for 28.3% of the total blasting accidents. It can be seen that toxic gas is one of the important causes of death accidents in the underground, and it must be paid enough attention to this.
1. The main components and harmfulness of toxic gases in gunpowder
In the artillery smoke generated by explosives, the main components of toxic gases are carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. If the explosive contains sulfur or sulfide, toxic gases such as hydrogen sulfide and sulfuric anhydride are formed during the explosion. These gases are extremely harmful. When the human body inhales a certain amount of toxic gas, it can cause headache, heart palpitations, vomiting, weakness of the limbs, fainting, and heavy convulsions, respiratory pauses, and even death.
2. Control measures for toxic gases
1) Preferred explosives and strict control of a single explosive charge
In the process of tunnel blasting, the explosives should be selected according to the actual situation of the working face. For example, when working area water, water-resistant explosives should be used. Otherwise, a large amount of toxic gas will be generated due to the dampness of the explosives and the stable propagation of the detonation. For the construction of low temperature freezing wells, antifreeze type explosives should be used, otherwise the explosives will be interrupted by incomplete explosion or detonation, resulting in a large amount of toxic gases. The amount of toxic gas generated by blasting is directly proportional to the amount of explosives, and the amount of blasting charge can be strictly controlled, which can effectively reduce the amount of toxic gas generated by blasting.
2) Control the weight of the outer shell material of the explosive
In order to prevent moisture, powdered explosives are usually wrapped in a stenciled paper shell. Since both paper and wax are combustible materials, the oxygen in the explosive is taken up, and the explosive is reacted negatively in the event of an explosion. In the case where the amount of oxygen is not sufficient, more carbon monoxide gas will be generated, and therefore, the weight of the paper shell and the amount of wax applied per 100 g of the explosive are not more than 2 g and 2.5 g, respectively.
3) Guarantee the clogging length and clogging quality of the blasthole
To ensure the clogging length and the quality of the clogging, the explosive can be exploded. Before the medium is broken, the high temperature and high pressure state are maintained in the charging hole, which is beneficial to the full reaction of the explosive and reduce the amount of toxic gas generated. Moreover, sufficient clogging length and good clogging quality will also reduce the unreacted or insufficiently reacted explosive particles throwing the reaction zone from the charging surface, and also reduce the toxic gas content in the air.
4) Using water seal blasting or shooting spray
When the explosive explodes, a high temperature and high pressure environment will be formed. The water mist generated during the water seal explosion will react with carbon monoxide to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen under high temperature and high pressure, which can effectively reduce the concentration of carbon monoxide in the gun smoke. Since some toxic gases generated by blasting are easily soluble in water, spraying with an automatic spray device can reduce the dust content and effectively reduce the toxic gas content and reduce the toxicity of the gun.
5) Adopt reverse detonation
When the reverse detonation method is adopted, the time when the mucus starts to move is delayed than the positive detonation, which indirectly increases the length of the clogging of the blasthole, so that the explosive reaction is completely improved, thereby reducing the amount of toxic gas generated.
3, local ventilation
The boring work surface is generally not equipped with fresh air by the ventilator installed on the ground. In order to make the boring work surface have enough fresh air for the staff to breathe, dilute and eliminate the gun smoke, dilute and eliminate toxic and harmful gases, Heat and water vapor, etc., install a local fan in the roadway at a certain distance from the heading face, and connect the air duct to the air outlet of the local fan to send the wind to the heading face. The local ventilator is responsible for the important task of supplying air to the heading face all day and night. Therefore, each local ventilator must be managed by the designated personnel, and the following management system should be strictly implemented.
1) It must be ensured that the local ventilator is always running. No matter whether the boring face is in normal production or handover, it is not allowed to stop the wind at will. It is necessary to ensure sufficient air volume for the boring face.
2) When the wind is stopped due to maintenance, power failure, etc., the personnel must be evacuated to cut off the power of all equipment in the working face. Therefore, the local ventilator and the electrical equipment in the heading face must be equipped with wind power locking devices.
3) Before the ventilation is restored, it is not allowed to send electricity and enter the work; before the ventilation is restored, the gas must be inspected, and the gas concentration in the wind flow within 10 meters near the local ventilation machine and the switch site must not exceed 0.5% before the local fan can be manually activated. .
4) Press-in local ventilator and starting device must be installed in the air inlet roadway, no less than 10 meters from the return air outlet to avoid circulating wind.
5) The local ventilator must be responsible for the start or stop of the local ventilator. Other personnel are not allowed to start or stop the local ventilator without permission.
6) The air cylinder must be hung on the side of the roadway. In the roadway, the shed, the cart, and the material handling equipment should not be damaged. When the gun is fired, the air cylinder cannot be broken. The air cylinder should be hung, straightened, and sturdy. The corner should be gentle. Do not wrinkle the air duct. Use the same specifications of the air duct.
7) After the local ventilator is turned on, the blades turn very fast. Do not put your hands in, and you can't put things like wooden sticks into it.
8) If the same tube is found to be broken, report the ventilation personnel immediately so that it can be repaired immediately to avoid air leakage and affect the ventilation of the driving face. Everyone in the well should take care of the local ventilator and the same cylinder, because it is the health, personal safety and safe production of the boring face and related personnel, so everyone should pay attention to the operation of the local ventilator and find abnormal conditions. Immediately report the ventilator or dispatch room for immediate processing.
4, single headed into the gun poisoning prevention measures
1) All the single-head tunneling operations must use mechanical ventilation, use the fan to connect the air duct to extract the gun smoke, and prohibit the use of high-pressure wind for ventilation;
2) Single-type ventilation can be used for the single-head tunneling length less than 100m, and mixed ventilation (that is, mixing and pressing) can be used for more than 100m.
3) The press-in fan should be installed in the upper air flow not less than 10m, and the end of the extraction type air duct should be connected to the lower air flow not less than 10m or directly into the return air duct. The distance between the fan air duct mouth and the working surface is not more than 10m, the pull-out type is not more than 5m, the mixed type air inlet air duct is not more than 10m, and the suction type air duct suction port should be more than 5m behind the press-in type air duct outlet.
4) The connection between the fan and the air cylinder, the connection between the air cylinder and the air cylinder, must ensure the quality, ensure straight, no air leakage, the corner should be smooth, the joint should be strict;
5) The rope lifting must use the traction rope. The position of the air cylinder installation must ensure that it does not affect the normal production operation.
6) When multiple fans are used to extract the gun smoke, the fan air ducts can be connected as a whole, but the power of the fan close to the head should be as large as possible. The starter fan should first start one close to the head and start in turn.
7) After the air cylinder is installed, it is necessary to strengthen the daily maintenance, management, and local air leakage points. The air duct that must be glued and cannot be refilled must be replaced by the entire air duct.
8) The same fan can only use the air tube of the same diameter. When the tunnel section allows, try to use the large diameter air duct to shorten the gun smoke discharge time.
9) The installed fan and air duct must be inspected and confirmed by a special person every day. The problem is immediately dealt with to ensure normal operation and ensure safe ventilation.
10) For blind mid-section construction, after the excavation on the patio, when the fan cannot be supported, the high-pressure wind can be used for ventilation. After the conditions are met, the fan must be installed immediately.
11) For high-patio work, if it is more than 30m, high-pressure air ventilation can be used appropriately.
Electric shock accident
1. Types and laws of electric shock accidents
1) Most of the electric shock accidents occur because people directly touch the charged body or come into contact with equipment that leaks due to insulation damage. Standing around the ground fault point, it may also be known as an electric shock. Electric shock can be divided into the following types:
a. People directly contact the electrified body for electric accidents
According to the way the human body touches the charged body and the way the current passes through the human body, such accidents can be divided into single-phase electric shock and two-phase electric shock. Single-phase electric shock refers to an accident that occurs when the human body touches a phase of a charged body on the ground or other grounding conductor. Two-phase electric shock refers to an accident that occurs when two human bodies touch two charged bodies at the same time, which is dangerous. Such accidents account for more than 40% of all electric shock accidents.
b. Electric shock accidents in contact with insulated and damaged electrical equipment
Under normal circumstances, the metal casing of electrical equipment is uncharged. When the insulation is damaged and the power is leaked, the electric shock may occur. The electric shock is the same as the contact with the electrified body. Such accidents account for more than 50% of all electric shock accidents.
c. Step voltage electric shock accident
When the grounded current of the charged body flows into the ground, the current produces a voltage drop around the grounding point, and a voltage drop occurs between the two feet around the grounding point, which causes the stride voltage to be electrically shocked.
2) The occurrence of electric shock accidents is sudden and causes serious consequences in a relatively short period of time, resulting in a high mortality rate. According to the statistical analysis of electric shock accidents, the law can be summarized as the following points.
a. Has a distinct seasonality. June-September of each year is a frequent season of electric shock accidents. This is because the rainy and humid period of this period is low, and the insulation performance of electrical equipment is degraded. At the same time, due to the hot weather, the clothing is single and sweaty, which increases the possibility of electric shock.
b. Low-voltage equipment has many electric shocks. This is due to the wide distribution of low-voltage power grids, low-voltage equipment and relatively simple, poor management, and many opportunities for people to contact.
c. Young and non-electrical electric shocks are numerous. These people have insufficient electrical safety knowledge, and the technology is not mature enough to cause electric shock accidents.
d. Portable and mobile devices have many electric shocks. This is because such devices need to move frequently, work conditions are poor, and it is prone to failure.
e. There are many electric shock accidents in metallurgy, mining and machinery industries. The work scenes in these industries are chaotic, the temperature is high, the humidity is high, there are many mobile devices, and there are many temporary lines, which is difficult to manage.
2, the danger of electric shock
It is well known that electric shock is when people come into contact with charged objects and the human body becomes part of the current path. The human body is an electric conductor. When a current is passed, the human body's cell tissue is destroyed by the action of electric current, causing thermal, mechanical, chemical and physiological effects. Electric shock can be divided into two major categories of electric shock and electric shock.
1) Electric shock
Electric shock is the most dangerous electric shock accident, and most electric shock deaths are caused by electric shock. When a person directly touches a charged body, current passes through the human body, causing numbness and twitching of the muscle. If it cannot be immediately removed from the power source, the nerve center of the human body will be harmed, causing difficulty in breathing, paralysis of the heart, and death.
2) Electric injury
Electrical injury is the damage caused by the thermal, chemical or mechanical effects of current. Electrical injuries are more common on the external surface of the human body and leave scars on the surface of the human body. Among them, arc burn is the most common and most serious, which can cause disability or fatality. In addition, there are electrocautery, burns, metallization of the skin and so on.
3, electric shock protection measures
Effective prevention of electric shock accidents requires both technical measures and organizational management measures. The following aspects can be summarized.
1) Prevent contact with live parts
Insulation, screen protection and safe spacing are the most common safety measures.
a. Insulation. That is, the electrically insulating body is sealed with a non-conductive insulating material, which is a basic protective measure for preventing direct contact with electricity. However, it should be noted that the insulation properties of the insulation material are consistent with the voltage, current carrying capacity, ambient environment and operating conditions of the equipment.
b. Screen protection. That is, the cover body, the shield, the cover, the box brake, etc. are used to isolate the charged body from the outside world. Such screen guards are used in places where electrical equipment is not convenient for insulation or insulation to ensure safety, and is an important measure to prevent human body from coming into contact with live parts.
c. Spacing. In order to prevent the body from touching or approaching the charged body, and preventing objects such as vehicles from colliding or excessively approaching the charged body, a certain safe distance should be maintained between the charged body and the charged body, the charged body and the ground, the charged body and other equipment and facilities. The size of the spacing is related to factors such as voltage level, device type, and installation method.
2) Prevent electrical equipment from leaking electricity and injuring people
Protective grounding and protection to zero are the basic technical measures to prevent contact with electricity.
a. Protective grounding. The uncharged metal parts of the normally functioning electrical equipment are tightly connected to the earth. The principle is to limit the grounding voltage of the leakage device to a safe range by grounding to prevent electric shock accidents. The protective earthing is suitable for the electrical equipment housing in the high-voltage power grid with a voltage higher than 1KV in the ungrounded neutral grid. Protective grounding should also be adopted.
b. Protection is connected to zero. In the 380/220V three-phase four-wire power supply system, the metal casing of the electrical equipment that is normally uncharged is closely connected with the neutral line in the power grid. The principle is that when the device is leaking, the current is short-circuited through the outer casing of the device and the zero-line single-phase. The short-circuit current blows the fuse or trips the automatic switch, thereby cutting off the power supply and eliminating the risk of electric shock. Suitable for low voltage systems where the neutral point of the grid is grounded.
3) Adopt safe voltage
According to the characteristics of the production and operation sites, the use of the corresponding level of safety voltage is a fundamental measure to prevent electric shock and casualties. The national standard "Safety Voltage" (GB3805-83) stipulates that the rating of China's safety voltage rating is 42V, 36V, 24V, 12V and 6V, which should be based on the working site, operator conditions, usage mode, power supply mode, line condition and other factors. Use. The safety voltage has certain limitations and is suitable for small electrical equipment such as hand-held power tools.
4) Leakage protection device
Leakage protection device, also known as electric shock safety device, can immediately send out an alarm signal and quickly cut off the power automatically when electrical equipment and lines are leaking or electric shock in the low-voltage power grid, thus protecting personal safety. Leakage protection devices can be divided into four types according to the action principle: voltage type, zero sequence current type, leakage current type and neutral point type. Among them, voltage type and zero sequence current type are widely used.
5) Reasonable use of protective equipment
In electrical work, reasonable matching and use of insulating protective equipment is of great significance to prevent electric shock accidents and to ensure the safety and health of operators in the production process. Insulation protective equipment can be divided into two categories, one is basic safety protective equipment, such as insulating rods, insulating pliers, high-voltage electroscope, etc.; the other is auxiliary safety equipment, such as insulating gloves, insulation (boots) shoes, rubber mats , insulation table, etc.
6) Safety electricity organization measures
To prevent electric shock accidents, technical measures are very important, and organizational management measures are also essential. These include the development of safe electricity measures plans and regulations, safety inspections, education and training, organization of accident analysis, and establishment of safety data files.
4. The main measures to prevent electric shock are:
1) Electrical workers must be highly responsible for safety. They should conscientiously implement relevant safety work procedures, and safety technical measures must be implemented. The electrical installation must comply with the insulation and isolation requirements, and the electrical equipment must be thoroughly cleaned. Be sure to effectively ground the metal casing of electrical equipment. Electrical workers should use safety tools such as insulated gloves, shoes, pads, clamps, rods, and electroscopes.
2) Strengthen the education of electric shock prevention for all employees, improve the awareness of electric shock prevention for all employees; improve the safe electricity use system; prohibit unlicensed personnel from engaging in electrician operations; strictly implement safety regulations for operating equipment and using electrical equipment.
3) Take precautions against the high peaks of electric shock accidents with seasonal characteristics. According to relevant information, electric shock accidents occurred in June, July, August and September accounted for about 70% of the total number of accidents in the whole year, and the number of accidents in July accounted for more than 40% of the peak period of the accident. Before the arrival of the hot and rainy season, it is necessary to fully organize the electrical safety inspection, and the mobile power tools should be included in the key inspection. Also do daily maintenance and inspection of electrical equipment.
5, electric shock emergency
In actual work and life, it is impossible to completely avoid electric shock accidents. Therefore, the timely rescue of electric shock and the correctness of treatment methods are the key to saving the lives of electric shock absorbers.
1) Rescue in time
a. Quickly disconnect the electric shock from the power supply.
B. When the electric shocker is disconnected from the power supply, it should be promptly symptomatic and ambulance depending on the specific situation. The main ambulance methods for on-site application are artificial respiration and extrathoracic heart compression.
c. According to the specific symptoms and development trend of the electric shock, the drug can be supplemented at the appropriate time.
2) The first aid method is correct
a quickly disconnected from the power supply
Turn off the power switch, or use an electrician's pliers or a wooden axe to cut the wire to disconnect the power.
If it is difficult to disconnect from the switch or disconnect the power supply, use dry wooden sticks, bamboo poles, etc. to pick up the wires or live parts of the electric shock absorbers; or use insulators to pull the electric shocker away.
b. On-site first aid measures
When the electric shocker is disconnected from the power supply, different first-aid measures should be taken according to the severity of the electric shock.
如果触电者å—的伤害ä¸ä¸¥é‡ï¼Œç¥žå¿—还清醒,åªæ˜¯å››è‚¢å‘麻ã€å…¨èº«æ— 力,或虽曾一度æ˜è¿·ï¼Œä½†æœªå¤±åŽ»çŸ¥è§‰è€…,都è¦ä½¿ä¹‹å°±åœ°å®‰é™ä¼‘æ¯1-2h,并严密观察。
如果触电者å—的伤害较严é‡ï¼Œæ— çŸ¥è§‰ï¼Œæ— å‘¼å¸ï¼Œä½†å¿ƒè„有跳动时,应立å³è¿›è¡Œäººå·¥å‘¼å¸ã€‚如有呼å¸ï¼Œä½†å¿ƒè„åœæ¢è·³åŠ¨ï¼Œåˆ™åº”采用胸外心è„挤压法。
如果触电者å—的伤害很严é‡ï¼Œå¿ƒè·³å’Œå‘¼å¸éƒ½å·²åœæ¢ï¼Œçž³å”放大,失去知觉,则须åŒæ—¶é‡‡å–人工呼å¸å’Œèƒ¸å¤–心è„挤压两ç§æ–¹æ³•ã€‚
åšäººå·¥å‘¼å¸å’Œèƒ¸å¤–挤压è¦æœ‰è€å¿ƒï¼Œå¹¶åšæŒæŠ¢æ•‘,直到把人救活,或者确诊已ç»æ»äº¡æ—¶ä¸ºæ¢ã€‚
在é€åŒ»é™¢æŠ¢æ•‘途ä¸ï¼Œä¸èƒ½ä¸æ–急救工作。
c.å£å¯¹å£(é¼»)人工呼å¸æ³•
施行å£å¯¹å£äººå·¥å‘¼å¸å‰ï¼Œåº”迅速将触电者身上障ç¢å‘¼å¸çš„衣领ã€ä¸Šè¡£ã€è£¤å¸¦è§£å¼€ï¼Œå¹¶è¿…速å–出触电者å£è…”内妨ç¢å‘¼å¸çš„食物,脱è½çš„å‡ç‰™ã€è¡€å—ã€ç²˜æ¶²ç‰ï¼Œä»¥å…å µå¡žå‘¼å¸é“。
作å£å¯¹å£(é¼»)人工呼å¸æ—¶ï¼Œåº”使触电者仰å§ï¼Œå¹¶ä½¿å…¶å¤´éƒ¨å……分åŽä»°ï¼Œ(最好一åªæ‰‹æ‰˜åœ¨è§¦ç”µè€…颈åŽ),使鼻å”æœä¸Šï¼Œä»¥åˆ©å‘¼å¸é“畅通。
å£å¯¹å£(é¼»)人工呼å¸æ³•æ“作æ¥éª¤å¦‚下:
(1)使触电者鼻å”(或嘴)ç´§é—,救护人员深å¸ä¸€å£æ°”åŽç´§è´´è§¦ç”µè€…çš„å£(或鼻)å‘内å¹æ°”,为时约2秒钟;
(2)å¹æ°”完毕,立å³ç¦»å¼€è§¦ç”µè€…çš„å£(或鼻),并æ¾å¼€è§¦ç”µè€…çš„é¼»å”(或嘴唇),让他自行呼气,为时约3秒钟。
å¦‚æžœæ— æ³•ä½¿è§¦ç”µè€…çš„å˜´å¼ å¼€ï¼Œå¯æ”¹ç”¨å£å¯¹é¼»äººå·¥å‘¼å¸æ³•ã€‚
d.胸外心è„挤压法
应使触电者抑å§åœ¨æ¯”较åšå®žçš„地方,姿势与å£å¯¹å£(é¼»)人工呼å¸æ³•ç›¸åŒã€‚动作è¦é¢†å¦‚下:
(1)救护人员跪在触电者一侧或骑跪在其腰部两侧,两手相å ï¼Œæ‰‹æŽŒæ ¹éƒ¨åœ¨å¿ƒçªä¸Šæ–¹ï¼Œèƒ¸éª¨ä¸‹ä¸‰åˆ†ä¹‹ä¸€è‡³äºŒåˆ†ä¹‹ä¸€å¤„。
(2)æŽŒæ ¹ç”¨åŠ›åž‚ç›´å‘下(脊背方å‘)挤压,对æˆäººåº”压陷3-4厘米,以æ¯ç§’ç§æŒ¤åŽ‹ä¸€æ¬¡ï¼Œæ¯åˆ†é’ŸæŒ¤åŽ‹60次为宜。
(3)挤压åŽæŽŒæ ¹å¾ˆå¿«æŠ¬èµ·ï¼Œè®©è§¦ç”µäººèƒ¸å»“自动å¤åŽŸã€‚æ¯æ¬¡æ”¾æ¾æ—¶ï¼ŒæŽŒæ ¹ä¸å¿…完全离开胸膛。
车辆伤害事故
机电è¿è¾“是矿井生产环节的é‡è¦ç»„æˆéƒ¨åˆ†ï¼Œå®ƒè´¯ç©¿äº†çŸ¿äº•çš„å„个生产环节,战线长,涉åŠé¢å¹¿ï¼Œç‰¹æ®Šå·¥ç§å¤šï¼ŒæŠ€æœ¯æ€§å¼ºã€‚æ ¹æ®å…¨å›½çŸ¿å±±é‡å¤§äº‹æ•…的调查分æžæ˜¾ç¤ºï¼Œæœºç”µäº‹æ•…在å„ç§äº‹æ•…ä¸å±…第4ä½ï¼Œè¿è¾“事故å 总事故数的20%~30%。
1ã€è½¦è¾†ä¼¤å®³äº‹æ•…频å‘çš„åŽŸå› å‰–æž
(1)特ç§ä½œä¸šäººå‘˜å®‰å…¨æ„识淡薄,麻痹大æ„ï¼Œæ²¡æœ‰ç‰¢å›ºæ ‘ç«‹"安全第一"çš„æ€æƒ³ï¼Œè¿å了"三大规程"åŠæœ‰å…³å®‰å…¨è§„定,è¿ç« 指挥ã€è¿ç« æ“作时有å‘生。
(2)特ç§ä½œä¸šäººå‘˜æ–‡åŒ–程度å‚å·®ä¸é½ï¼ŒæŽŒæ¡ç‰¹ç§ä½œä¸šæŠ€æœ¯ä¸å¨´ç†Ÿã€‚对技术工ç§å®‰å…¨æ“作知识掌æ¡ä¸ç‰¢ï¼Œç†Ÿæ‚‰ç¨‹åº¦ä¸å¤Ÿï¼Œæ˜¯é€ æˆå¤šå‘事故的é‡è¦åŽŸå› 。特别是部分人员文化基础差,å¦ä¹ 业务技术的积æžæ€§å·®ï¼Œç´ è´¨æžä½Žï¼Œç»™æœºç”µè¿è¾“安全带æ¥äº†æžå¤§éšæ‚£ã€‚
(3)指令性的临时工顶替。由于代岗人员顶替时间çŸï¼Œå¯¹é¡¶æ›¿å·¥ç§æ“作熟练程度差,缺ä¹é¡¶å²—å‰çš„安全培è®ï¼Œäº§ç”Ÿè¿ç« 指挥和盲目æ“作åŒé‡ä¸å®‰å…¨å› ç´ ã€‚
(4)特ç§ä½œä¸šäººå‘˜çš„频ç¹è°ƒæ¢ï¼Œå²—ä½çš„调整,给安全埋下éšæ‚£ã€‚特别作业人员大都是ç»è¿‡å½“地劳动部门专业培è®å–å¾—æ“作åˆæ ¼è¯åŽä½œä¸šè€…,对他们的工ç§ä¸å®œéšæ„予以å˜åŠ¨ã€‚å¦å¤–,临时性工作调整时安全培è®å·¥ä½œæ²¡æœ‰åŠæ—¶åˆ°ä½ä¹Ÿå¸¦æ¥äº†å®‰å…¨éšæ‚£ã€‚
(5)安全基础工作薄弱,安全å¯é æ€§å·®ã€‚ä¸€æ˜¯æ ‡å‡†åŒ–æ“作执行ä¸ä¸¥ï¼Œè€ƒæ ¸ä¸ä¸¥ï¼Œæœºè¿æ ‡å‡†åŒ–工作难以到ä½;二是特ç§ä½œä¸šäººå‘˜çš„安全培è®æ•™è‚²ä¸å¤Ÿï¼ŒæŠ€æœ¯ç´ 质得ä¸åˆ°æ高。
(6)安全制度ä¸ä¸¥ï¼Œé—留安全éšæ‚£ã€‚一是岗ä½è´£ä»»åˆ¶ä¸å¥å…¨ï¼Œå¯¹æŸäº›å·¥ä½œç›¸äº’扯皮,éšæ‚£å¾—ä¸åˆ°åŠæ—¶æ•´æ”¹è½å®ž;二是安全制度执行ä¸ä¸¥ï¼Œå¯¹å®‰å…¨è€ƒæ ¸ä¸å¤Ÿä¸¥åŽ‰;三是对事故处ç†æœªä¸¥æ ¼æŒ‰"三ä¸æ”¾è¿‡"原则分æžå¤„ç†ï¼Œå¤„罚太轻甚至层层ä¿æŠ¤ï¼Œä¸ä¸¥è‚ƒè¿½ç©¶è´£ä»»ï¼ŒèŒå·¥å—ä¸åˆ°æ•™è‚²ï¼Œé˜²èŒƒæŽªæ–½ä¸åˆ°ä½ï¼Œç»“果是事故é‡å¤å‘生。
2 预防车辆伤害事故措施
(1)统一æ€æƒ³è®¤è¯†ï¼ŒåšæŒ"安全第一"ä¸åŠ¨æ‘‡ã€‚"安全第一"是指如何看待和处ç†å®‰å…¨ä¸Žç”Ÿäº§ä»¥åŠä¸Žå…¶å®ƒå„项工作的关系。è¦å¼ºè°ƒå®‰å…¨ï¼Œçªå‡ºå®‰å…¨ï¼ŒæŠŠå®‰å…¨æ”¾åœ¨ä¸€åˆ‡å·¥ä½œçš„首è¦ä½ç½®ã€‚åŒæ—¶å„级领导åŠç”Ÿäº§å•ä½ï¼Œè¦æŠŠå®‰å…¨å½“作一项头ç‰å¤§äº‹æ¥æŠ“,时时事事把安全工作摆在高于一切ã€é‡äºŽä¸€åˆ‡ã€å…ˆäºŽä¸€åˆ‡çš„ä½ç½®ï¼Œå§‹ç»ˆåšæŒ"安全第一"ä¸åŠ¨æ‘‡ã€‚æœç»å¿½è§†å®‰å…¨çš„投入,设备带病è¿è¡Œï¼Œè¿ç« 冒险蛮干的现象。
(2)åŠ å¼ºç‰¹æ®Šå·¥ç§çš„用工制度管ç†ã€‚矿山机è¿å·¥ç§çš„技术性较强,其å„å²—ä½å·¥ç§éƒ½ä¸èƒ½ä»¥ç…§é¡¾çš„身份出现,è¦ç”±æ€æƒ³ç«¯æ£ã€æŠ€æœ¯å…¨é¢çš„工人æ¥æ‹…任。åŒæ—¶åŠ 强临时用工的安全管ç†ï¼Œå°½é‡å°‘用或ä¸ç”¨ä¸´æ—¶å·¥ã€‚除特殊情况外,特殊工ç§äººå‘˜ä¸èƒ½éšæ„è°ƒæ¢ï¼Œè¦ä¸¥æ ¼è€ƒæ ¸å‘è¯ï¼ŒæŒè¯ä¸Šå²—。
(3)åŠ å¼ºæ€æƒ³æ•™è‚²å·¥ä½œã€‚通过å„ç§é€”å¾„åŠ å¼ºå¼•å¯¼æ•™è‚²èŒå·¥ï¼Œæ˜Žç¡®äº‹æ•…çš„å±å®³æ€§ï¼Œæ¶ˆé™¤å®‰å…¨ä¾¥å¹¸å¿ƒç†ï¼Œå¢žå¼ºå®‰å…¨æ„识。è¿ç”¨å…¸åž‹çš„事故案例对èŒå·¥è¿›è¡Œæ€æƒ³æ•™è‚²ï¼Œç”¨ç”ŸåŠ¨çš„典型事故案例形象教育èŒå·¥ï¼Œæ•™è‚²èŒå·¥è®¤æ¸…"三è¿"çš„å±å®³ï¼Œå¼ºåŒ–èŒå·¥å®‰å…¨é˜²èŒƒæ„识,以引起èŒå·¥æ€æƒ³ä¸Šçš„共鸣。å¦å¤–,特别è¦æ³¨æ„了解掌æ¡èŒå·¥çš„æ€æƒ³å’Œç”Ÿç†çŠ¶æ€ï¼Œå› åœ°åˆ¶å®œï¼Œå› äººè€Œå¼‚ï¼ŒåŠ ä»¥ç›‘æŠ¤ï¼Œé˜²æ¢å› ä¸å®‰å…¨å¿ƒç†å› ç´ é€ æˆçš„çªç„¶äº‹æ•…å‘生。
(4)åŠ å¼ºèŒå·¥çš„安全业务培è®å·¥ä½œã€‚一是æ¯éš”一定时期组织èŒå·¥è¿›è¡ŒæŠ€æœ¯æ¯”æ¦ï¼Œå¯¹ä¼˜èƒœè€…给予é‡å¥–,以调动èŒå·¥å¦æŠ€æœ¯ã€å¦ä¸šåŠ¡çš„积æžæ€§ï¼Œä¿ƒä½¿ä»–们在岗ä½ä¸ŠæŒ‰æ ‡å‡†åŠè§„程进行作业;二是采用"三结åˆ"的培è®æ–¹å¼ï¼Œå³ä¸šä½™åŸ¹è®ä¸Žé‡ç‚¹åŸ¹è®ç›¸ç»“åˆï¼Œä»¥é‡ç‚¹åŸ¹è®ä¸ºä¸»ï¼Œå†…培与外培相结åˆï¼Œä»¥å†…培为主;对新工人ã€æ–°å²—ä½ã€æ–°æŠ€æœ¯è¦è¿›è¡Œå¼ºåŒ–培è®ï¼Œä»¥å…¨é¢æ高èŒå·¥çš„å®‰å…¨ä¸šåŠ¡ç´ è´¨ä¸ºç›®çš„ï¼Œä¸ºæžå¥½å®‰å…¨ç”Ÿäº§æ‰“下åšå®žçš„"以人为本"的基础。
(5)åŠªåŠ›åŠ å¼ºçŸ¿äº•è´¨é‡æ ‡å‡†åŒ–管ç†ã€‚矿井质é‡æ ‡å‡†åŒ–是矿山安全的基础。实践è¯æ˜Žï¼ŒçŸ¿äº•è´¨é‡æ ‡å‡†åŒ–工作的投入,能得到åå‡ å€ç”šè‡³å‡ åå€çš„效益产出,有力地促进了安全生产。è¦æŠŠè¿™é¡¹å·¥ä½œå½“作一项ç»å¸¸åŒ–的工作æ¥æŠ“,è¦ç”±é™æ€è¾¾æ ‡å‘动æ€è¾¾æ ‡è½¬å˜ï¼Œç”±é‡ç»“æžœå‘é‡è¿‡ç¨‹è½¬å˜ï¼Œå®žçŽ°ç”Ÿäº§å…¨è¿‡ç¨‹è¾¾æ ‡ã€‚
(6)åŠ å¼ºå®‰å…¨å·¥ä½œåŠ›åº¦ï¼Œå‘管ç†è¦å®‰å…¨ã€‚实践è¯æ˜Žï¼Œè¦æŠ“好安全工作,离ä¸å¼€æœ‰æ•ˆçš„监ç£ï¼Œå¤±åŽ»äº†ç›‘ç£ä½œç”¨ï¼Œå¿…然助长麻痹侥幸ã€è¿ç« 蛮干的现象。监ç£ä¸åˆ°ä½æˆ–æµäºŽå½¢å¼ï¼Œæ˜¯å¯¼è‡´å®‰å…¨äº‹æ•…çš„é‡è¦åŽŸå› ã€‚å› æ¤ï¼Œå¿…须强化监ç£åˆ¶çº¦æœºåˆ¶ï¼Œå……分å‘挥现场安监人员的作用;åŒæ—¶ï¼Œå¿…é¡»åšæŒè¡Œä¹‹æœ‰æ•ˆçš„安全管ç†åˆ¶åº¦ï¼Œç‰¹åˆ«æ˜¯è¦å»ºç«‹å’Œå®Œå–„å„级领导和业务部门的安全生产责任制和工人的岗ä½è´£ä»»åˆ¶ï¼Œæ˜Žç¡®æ¯ä¸ªäººçš„安全èŒè´£ã€‚å¦å¤–,采å–安全资金激励机制,通过ç»æµŽæ æ†ï¼Œä¸¥æ ¼è€ƒæ ¸ï¼Œå…‘现奖惩,从而促进å„项安全管ç†åˆ¶åº¦çš„è½å®žã€‚
矿井è¿è¾“事故
1.è¹¾ç½æ—¶ä¹˜å人员的自救与互救措施
è¹¾ç½æ˜¯çŸ¿äº•æå‡è¿è¾“ä¸å‘生较多的一ç§äº‹æ•…。它对乘å人员的伤害是å‘ç½ç¬¼åº•éƒ¨çš„强烈冲击,å¯é€ æˆè…¿éƒ¨éª¨æŠ˜ç‰åˆ›ä¼¤ã€‚è¹¾ç½æ—¶ä¹˜å人员的自救与互救措施是:
(1)常乘åç½ç¬¼çš„人员都知é“,当ç½ç¬¼ä¸‹é™åˆ°ç¦»åœç½ä½ç½®30多米处时,就è¦å‡é€Ÿã€‚当到达æ¤å¤„时还ä¸å‡
1. Material: Razor wire is usually made of hot dipped galvanized wire and steel plate. Or stainless steel wire and plate.
2. Outside diameter : 450mm, 500mm, 600mm, 700mm, 800mm, 900mm, 960mm, 980mm, etc.
3. Number of Loops: 33, 56
4. Clips: 3 or 5 or no clips.
5. Package: Inner proof paper, outside weave bag or Carton.
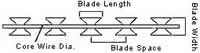
Reference Number
Blade Style
Thickness
Wire Dia
Barb Length
Barb Width
Barb spacing
BTO-12
0.5±0.05
2.5±0.1
10±1
13±1
26±1
BTO-18
0.5±0.05
2.5±0.1
15±1
15±1
33±1
BTO-22
0.5±0.05
2.5±0.1
22±1
15±1
34±1
CBT-65
0.6±0.05
2.5±0.1
65±2
21±1
100±2
Outside Diameter
No. of Loops
Standard Length per Coil
Type
Notes
450mm
33
8M
CBT-65
Single coil
500mm
41
10M
CBT-65
Single coil
700mm
41
10M
CBT-65
Single coil
960mm
53
13M
CBT-65
Single coil
500mm
102
16M
BTO-10.15.22
Cross type
600mm
86
14M
BTO-10.15.22
Cross type
700mm
72
12M
BTO-10.15.22
Cross type
800mm
64
10M
BTO-10.15.22
Cross type
960mm
52
9M
BTO-10.15.22
Cross type
![]()
![]()
![]()
Razor Blade Barbed Wire,Galvanized Razor Wire,Concertina Razor Wire,Galvanized Steel Razor Wire
Hebei Yicheng Wire Mesh Products Co., Ltd , https://www.yc-fence.com