[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Energy storage batteries based on water-based electrolytes have high safety, low cost, and excellent rate performance, and have developed rapidly in recent years. However, the electrochemical window of the aqueous electrolyte is narrow (1.23 V), which causes the working voltage of this type of battery to be generally low; and the choice of electrode materials for the aqueous battery is more stringent, and the stability and specific capacity need to be greatly improved. Bottlenecks such as low operating voltage and low energy density make large-scale applications of water-based batteries face huge challenges.
Electrolyte is a term with a wide meaning, which is widely used in different industries. There are electrolytes in the body (also called electrolytes), as well as electrolytes used in the battery industry, and electrolytes in electrolytic capacitors and supercapacitors.
The composition of electrolytes used in different industries varies greatly, or even completely different.
For example, the electrolyte of the human body is mainly composed of water and sodium chloride, PH buffer substances, etc. The electrolyte of aluminum electrolytic capacitors contains GBL and other major solvents, the supercapacitor electrolyte contains propylene carbonate or acetonitrile, and lithium manganese primary battery electrolysis The liquid contains main solvents such as propylene carbonate, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, and the lithium ion battery electrolyte contains main solvents such as ethylene carbonate, dimethyl carbonate, ethyl methyl carbonate, and diethyl carbonate. Their respective conductive salts It is also completely different, such as sodium chloride in the human body, tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate in supercapacitor electrolytes, lithium perchlorate or lithium triflate is commonly used in lithium manganese primary batteries, and lithium ion batteries are Lithium hexafluorophosphate.
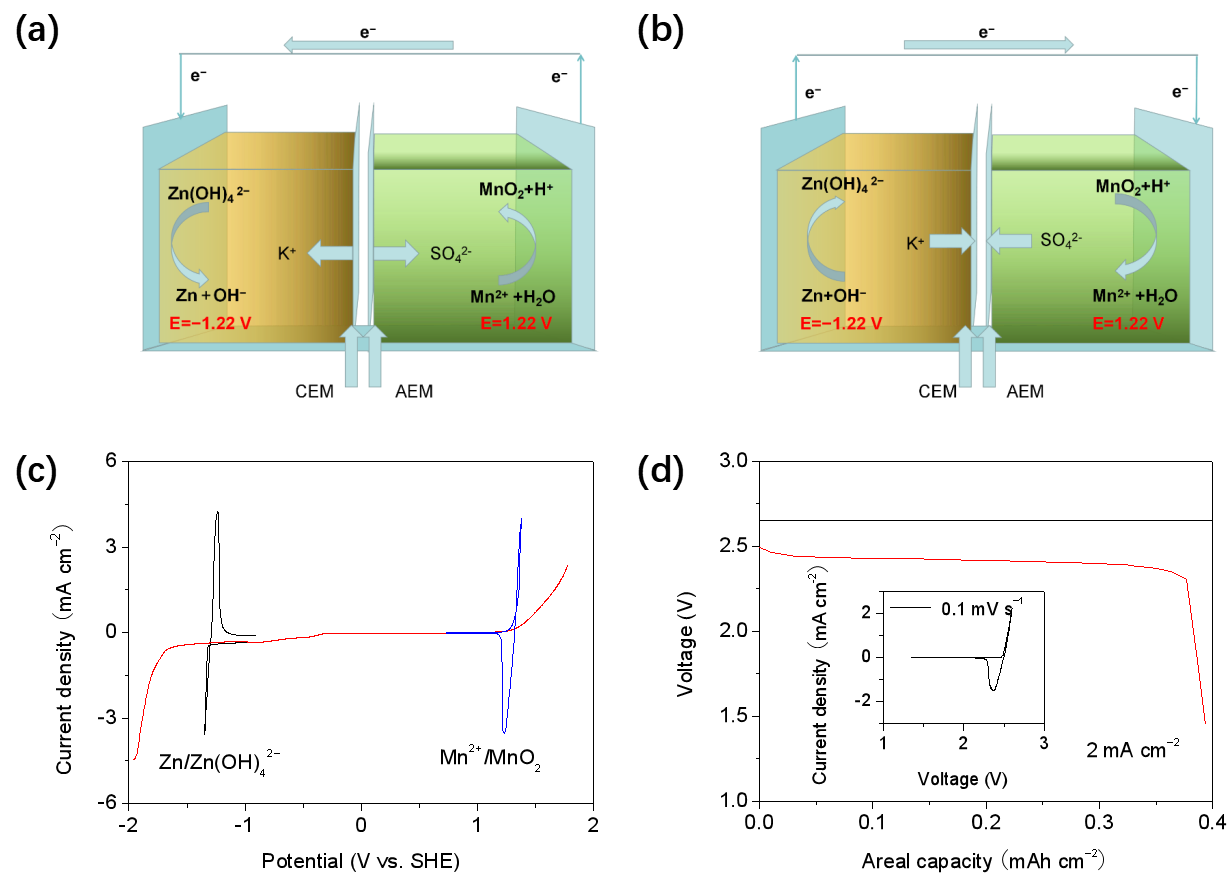
Recently, a research team led by Liu Yu and associate researcher Chi Xiaowei, a researcher at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, put forward the idea of ​​acid-base isolation electrolyte and dual dissolution / deposition electrode reaction to construct a class with high energy density (1503 Wh kg-1, a new type of water battery based on positive electrode active material). This system uses a bipolar membrane to isolate the acid-base electrolyte, and uses the dependence of the electrode potential on the pH of the electrolyte to widen the electrochemical stability window of the full battery electrolyte to 3 V. At the same time, the positive and negative electrodes of the battery are used. The dissolution / deposition reaction (negative electrode: Zn / Zn (OH) 42+; positive electrode: Mn2 + / MnO2), thus giving the positive and negative electrodes a theoretical specific capacity of up to 616 mAh g-1 and 820 mAh g-1.
Tests show that the battery has high Coulomb efficiency (98.4%), excellent cycle performance (capacity retention rate after 1500 laps is 97.5%), and rate characteristics.
Coulombic efficiency, also known as discharge efficiency, refers to the ratio of battery discharge capacity to charge capacity during the same cycle, that is, the percentage of discharge capacity to charge capacity. For the positive electrode material, it is the lithium insertion capacity / delithium capacity, that is, the discharge capacity / charge capacity; for the negative electrode material, it is the lithium removal capacity / lithium insertion capacity, that is, the charge capacity / discharge capacity.
The flow battery constructed based on the reaction system showed very little attenuation, and the capacity retention rate was 99.5% after 6,000 cycles. Relevant research results were published in Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, DOI: 10.1002 / aenm.201903589, and the cover of the journal was introduced. This research also provides new ideas for the development of high-voltage, high-specific-energy water batteries.
Source: Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Encyclopedia
Qingdao SUBA CNC Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.cncrouter-china.com